Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
DBSCAN聚类算法演示#
DBSCAN(基于密度的噪声应用空间聚类)在高密度区域中找到核心样本,并从中扩展聚类。 该算法适用于包含相似密度聚类的数据。
请参阅示例 在玩具数据集上比较不同的聚类算法 ,了解不同聚类算法在二维数据集上的演示。
数据生成#
我们使用 make_blobs 来创建 3 个合成簇。
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
centers = [[1, 1], [-1, -1], [1, -1]]
X, labels_true = make_blobs(
n_samples=750, centers=centers, cluster_std=0.4, random_state=0
)
X = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X)
我们可以将结果数据可视化:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1])
plt.show()
计算 DBSCAN#
可以使用 labels_ 属性访问 DBSCAN 分配的标签。噪声样本被赋予标签 math:-1 。
import numpy as np
from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.cluster import DBSCAN
db = DBSCAN(eps=0.3, min_samples=10).fit(X)
labels = db.labels_
# 标签中的簇数量,如果存在噪声则忽略。
n_clusters_ = len(set(labels)) - (1 if -1 in labels else 0)
n_noise_ = list(labels).count(-1)
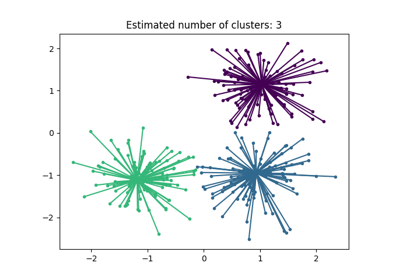
print("Estimated number of clusters: %d" % n_clusters_)
print("Estimated number of noise points: %d" % n_noise_)
Estimated number of clusters: 3
Estimated number of noise points: 18
聚类算法本质上是无监督学习方法。然而,由于 make_blobs 提供了合成簇的真实标签,因此可以使用利用这种“监督”真实信息的评估指标来量化生成簇的质量。这类指标的例子包括同质性、完整性、V-测度、兰德指数、调整兰德指数和调整互信息(AMI)。
如果不知道真实标签,只能使用模型结果本身进行评估。在这种情况下,轮廓系数非常有用。
有关更多信息,请参见 聚类性能评估中的机会调整 示例或 clustering_evaluation 模块。
print(f"Homogeneity: {metrics.homogeneity_score(labels_true, labels):.3f}")
print(f"Completeness: {metrics.completeness_score(labels_true, labels):.3f}")
print(f"V-measure: {metrics.v_measure_score(labels_true, labels):.3f}")
print(f"Adjusted Rand Index: {metrics.adjusted_rand_score(labels_true, labels):.3f}")
print(
"Adjusted Mutual Information:"
f" {metrics.adjusted_mutual_info_score(labels_true, labels):.3f}"
)
print(f"Silhouette Coefficient: {metrics.silhouette_score(X, labels):.3f}")
Homogeneity: 0.953
Completeness: 0.883
V-measure: 0.917
Adjusted Rand Index: 0.952
Adjusted Mutual Information: 0.916
Silhouette Coefficient: 0.626
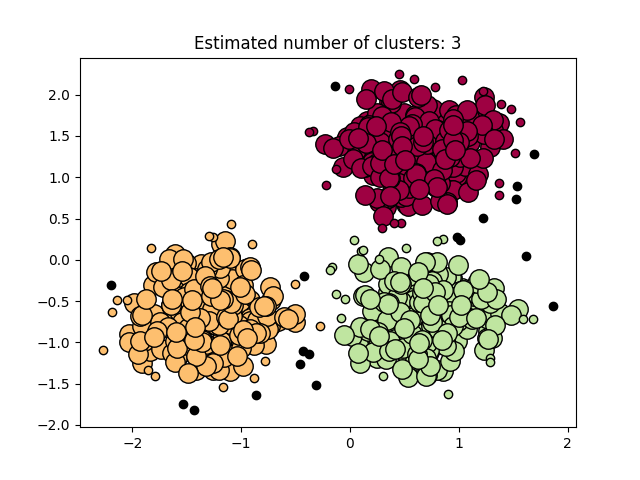
绘制结果#
核心样本(大点)和非核心样本(小点)根据分配的簇进行颜色编码。被标记为噪声的样本用黑色表示。
unique_labels = set(labels)
core_samples_mask = np.zeros_like(labels, dtype=bool)
core_samples_mask[db.core_sample_indices_] = True
colors = [plt.cm.Spectral(each) for each in np.linspace(0, 1, len(unique_labels))]
for k, col in zip(unique_labels, colors):
if k == -1:
# 黑色用于噪声。
col = [0, 0, 0, 1]
class_member_mask = labels == k
xy = X[class_member_mask & core_samples_mask]
plt.plot(
xy[:, 0],
xy[:, 1],
"o",
markerfacecolor=tuple(col),
markeredgecolor="k",
markersize=14,
)
xy = X[class_member_mask & ~core_samples_mask]
plt.plot(
xy[:, 0],
xy[:, 1],
"o",
markerfacecolor=tuple(col),
markeredgecolor="k",
markersize=6,
)
plt.title(f"Estimated number of clusters: {n_clusters_}")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.082 seconds)
Related examples