Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
稳健与经验协方差估计#
通常的协方差最大似然估计对数据集中的异常值非常敏感。在这种情况下,最好使用稳健的协方差估计器,以保证估计对数据集中的“错误”观测值具有抵抗力。[1], [2]
最小协方差行列式估计器#
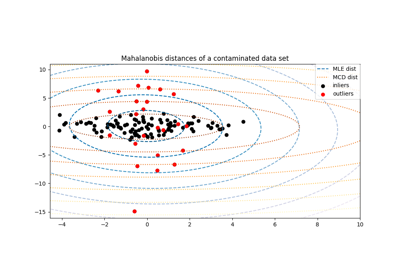
最小协方差行列式估计器是一种稳健的、高崩溃点(即它可以用于估计高度污染数据集的协方差矩阵,最多可容忍 \(\frac{n_\text{samples} - n_\text{features}-1}{2}\) 个异常值)的协方差估计器。其思想是找到 \(\frac{n_\text{samples} + n_\text{features}+1}{2}\) 个观测值,其经验协方差具有最小的行列式,从而得到一个“纯净”的观测子集,用于计算位置和协方差的标准估计。在一个旨在补偿估计仅从初始数据的一部分学习到的校正步骤之后,我们最终得到数据集位置和协方差的稳健估计。
最小协方差行列式估计器(MCD)由P.J.Rousseuw在[3]_中引入。
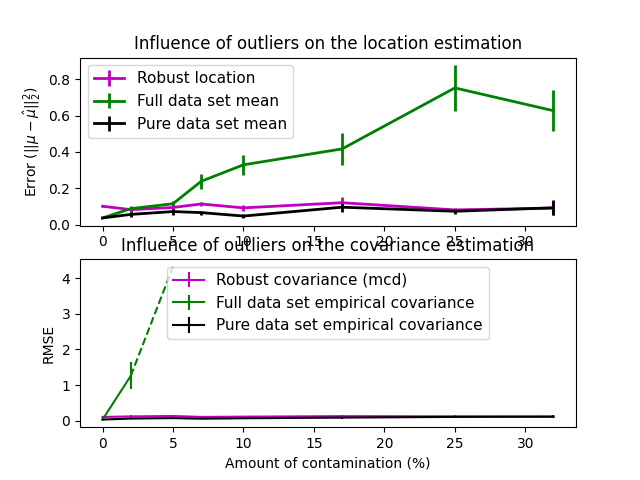
评估#
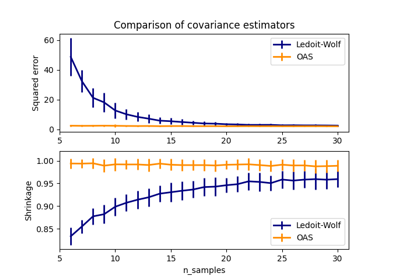
在这个例子中,我们比较了在使用各种类型的位置和协方差估计对受污染的高斯分布数据集进行估计时所产生的误差:
全数据集的均值和经验协方差,一旦数据集中有异常值就会崩溃
稳健的MCD,只要 \(n_\text{samples} > 5n_\text{features}\) ,其误差较低
已知是良好观测值的观测值的均值和经验协方差。这可以被认为是“完美”的MCD估计,因此可以通过与这种情况进行比较来信任我们的实现。
参考文献#
import matplotlib.font_manager
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.covariance import EmpiricalCovariance, MinCovDet
# example settings
n_samples = 80
n_features = 5
repeat = 10
range_n_outliers = np.concatenate(
(
np.linspace(0, n_samples / 8, 5),
np.linspace(n_samples / 8, n_samples / 2, 5)[1:-1],
)
).astype(int)
# 定义数组以存储结果
err_loc_mcd = np.zeros((range_n_outliers.size, repeat))
err_cov_mcd = np.zeros((range_n_outliers.size, repeat))
err_loc_emp_full = np.zeros((range_n_outliers.size, repeat))
err_cov_emp_full = np.zeros((range_n_outliers.size, repeat))
err_loc_emp_pure = np.zeros((range_n_outliers.size, repeat))
err_cov_emp_pure = np.zeros((range_n_outliers.size, repeat))
# 计算
for i, n_outliers in enumerate(range_n_outliers):
for j in range(repeat):
rng = np.random.RandomState(i * j)
# 生成数据
X = rng.randn(n_samples, n_features)
# 添加一些异常值
outliers_index = rng.permutation(n_samples)[:n_outliers]
outliers_offset = 10.0 * (
np.random.randint(2, size=(n_outliers, n_features)) - 0.5
)
X[outliers_index] += outliers_offset
inliers_mask = np.ones(n_samples).astype(bool)
inliers_mask[outliers_index] = False
# 拟合最小协方差行列式(MCD)稳健估计器到数据
mcd = MinCovDet().fit(X)
# 将原始稳健估计与真实位置和协方差进行比较
err_loc_mcd[i, j] = np.sum(mcd.location_**2)
err_cov_mcd[i, j] = mcd.error_norm(np.eye(n_features))
# 比较从完整数据集中学习到的估计量与真实参数。
err_loc_emp_full[i, j] = np.sum(X.mean(0) ** 2)
err_cov_emp_full[i, j] = (
EmpiricalCovariance().fit(X).error_norm(np.eye(n_features))
)
# 与从纯数据集(即“完美”mcd)中学习到的经验协方差进行比较
pure_X = X[inliers_mask]
pure_location = pure_X.mean(0)
pure_emp_cov = EmpiricalCovariance().fit(pure_X)
err_loc_emp_pure[i, j] = np.sum(pure_location**2)
err_cov_emp_pure[i, j] = pure_emp_cov.error_norm(np.eye(n_features))
# 显示结果
font_prop = matplotlib.font_manager.FontProperties(size=11)
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
lw = 2
plt.errorbar(
range_n_outliers,
err_loc_mcd.mean(1),
yerr=err_loc_mcd.std(1) / np.sqrt(repeat),
label="Robust location",
lw=lw,
color="m",
)
plt.errorbar(
range_n_outliers,
err_loc_emp_full.mean(1),
yerr=err_loc_emp_full.std(1) / np.sqrt(repeat),
label="Full data set mean",
lw=lw,
color="green",
)
plt.errorbar(
range_n_outliers,
err_loc_emp_pure.mean(1),
yerr=err_loc_emp_pure.std(1) / np.sqrt(repeat),
label="Pure data set mean",
lw=lw,
color="black",
)
plt.title("Influence of outliers on the location estimation")
plt.ylabel(r"Error ($||\mu - \hat{\mu}||_2^2$)")
plt.legend(loc="upper left", prop=font_prop)
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
x_size = range_n_outliers.size
plt.errorbar(
range_n_outliers,
err_cov_mcd.mean(1),
yerr=err_cov_mcd.std(1),
label="Robust covariance (mcd)",
color="m",
)
plt.errorbar(
range_n_outliers[: (x_size // 5 + 1)],
err_cov_emp_full.mean(1)[: (x_size // 5 + 1)],
yerr=err_cov_emp_full.std(1)[: (x_size // 5 + 1)],
label="Full data set empirical covariance",
color="green",
)
plt.plot(
range_n_outliers[(x_size // 5) : (x_size // 2 - 1)],
err_cov_emp_full.mean(1)[(x_size // 5) : (x_size // 2 - 1)],
color="green",
ls="--",
)
plt.errorbar(
range_n_outliers,
err_cov_emp_pure.mean(1),
yerr=err_cov_emp_pure.std(1),
label="Pure data set empirical covariance",
color="black",
)
plt.title("Influence of outliers on the covariance estimation")
plt.xlabel("Amount of contamination (%)")
plt.ylabel("RMSE")
plt.legend(loc="upper center", prop=font_prop)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.836 seconds)
Related examples