Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
识别手写数字#
这个例子展示了如何使用scikit-learn来识别0-9的手写数字图像。
# 作者:scikit-learn 开发者
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
# 标准科学Python导入
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 导入数据集、分类器和性能指标
from sklearn import datasets, metrics, svm
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
数字数据集#
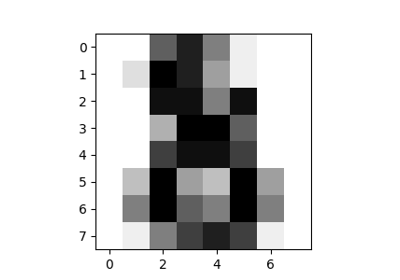
数字数据集由8x8像素的数字图像组成。数据集的 images 属性存储每个图像的8x8灰度值数组。我们将使用这些数组来可视化前4个图像。数据集的 target 属性存储每个图像所代表的数字,并将其包含在下面4个图的标题中。
注意:如果我们处理的是图像文件(例如 ‘png’ 文件),我们会使用 matplotlib.pyplot.imread 加载它们。
digits = datasets.load_digits()
_, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=4, figsize=(10, 3))
for ax, image, label in zip(axes, digits.images, digits.target):
ax.set_axis_off()
ax.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation="nearest")
ax.set_title("Training: %i" % label)

分类#
要在这些数据上应用分类器,我们需要将图像展平,将每个二维的灰度值数组从形状 (8, 8) 变为形状 (64,) 。随后,整个数据集的形状将变为 (n_samples, n_features) , 其中 n_samples 是图像的数量, n_features 是每个图像中的像素总数。
我们可以将数据分为训练集和测试集,并在训练样本上拟合支持向量分类器。随后,拟合的分类器可以用于预测测试集样本的数字值。
# 扁平化图像
n_samples = len(digits.images)
data = digits.images.reshape((n_samples, -1))
# 创建一个分类器:支持向量分类器
clf = svm.SVC(gamma=0.001)
# 将数据分为50%的训练子集和50%的测试子集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
data, digits.target, test_size=0.5, shuffle=False
)
# 学习训练子集上的数字
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 预测测试子集上的数字值
predicted = clf.predict(X_test)
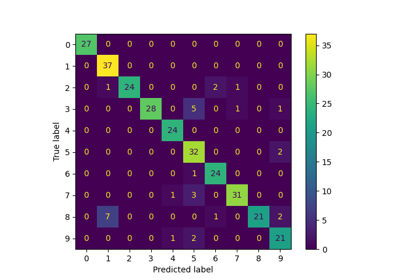
下面我们将可视化前四个测试样本,并在标题中显示它们的预测数字值。
_, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=4, figsize=(10, 3))
for ax, image, prediction in zip(axes, X_test, predicted):
ax.set_axis_off()
image = image.reshape(8, 8)
ax.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation="nearest")
ax.set_title(f"Prediction: {prediction}")

classification_report 构建一个文本报告,显示主要的分类指标。
print(
f"Classification report for classifier {clf}:\n"
f"{metrics.classification_report(y_test, predicted)}\n"
)
Classification report for classifier SVC(gamma=0.001):
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 0.99 0.99 88
1 0.99 0.97 0.98 91
2 0.99 0.99 0.99 86
3 0.98 0.87 0.92 91
4 0.99 0.96 0.97 92
5 0.95 0.97 0.96 91
6 0.99 0.99 0.99 91
7 0.96 0.99 0.97 89
8 0.94 1.00 0.97 88
9 0.93 0.98 0.95 92
accuracy 0.97 899
macro avg 0.97 0.97 0.97 899
weighted avg 0.97 0.97 0.97 899
我们还可以绘制一个真实数字值和预测数字值的: ref:混淆矩阵 <confusion_matrix> 。
disp = metrics.ConfusionMatrixDisplay.from_predictions(y_test, predicted)
disp.figure_.suptitle("Confusion Matrix")
print(f"Confusion matrix:\n{disp.confusion_matrix}")
plt.show()
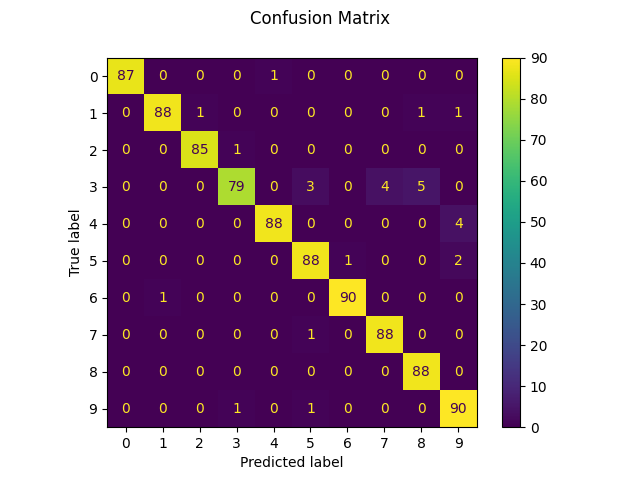
Confusion matrix:
[[87 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 88 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1]
[ 0 0 85 1 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 79 0 3 0 4 5 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 88 0 0 0 0 4]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 88 1 0 0 2]
[ 0 1 0 0 0 0 90 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 88 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 88 0]
[ 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 90]]
如果评估分类器的结果是以 混淆矩阵 的形式存储的,而不是以 y_true 和 y_pred 的形式存储的,仍然可以按如下方式构建 classification_report :
# The ground truth and predicted lists
#
#
y_true = []
y_pred = []
cm = disp.confusion_matrix
# 对于混淆矩阵中的每个单元格,将相应的真实值和预测值添加到列表中。
for gt in range(len(cm)):
for pred in range(len(cm)):
y_true += [gt] * cm[gt][pred]
y_pred += [pred] * cm[gt][pred]
print(
"Classification report rebuilt from confusion matrix:\n"
f"{metrics.classification_report(y_true, y_pred)}\n"
)
Classification report rebuilt from confusion matrix:
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 0.99 0.99 88
1 0.99 0.97 0.98 91
2 0.99 0.99 0.99 86
3 0.98 0.87 0.92 91
4 0.99 0.96 0.97 92
5 0.95 0.97 0.96 91
6 0.99 0.99 0.99 91
7 0.96 0.99 0.97 89
8 0.94 1.00 0.97 88
9 0.93 0.98 0.95 92
accuracy 0.97 899
macro avg 0.97 0.97 0.97 899
weighted avg 0.97 0.97 0.97 899
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.189 seconds)
Related examples