Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
非负最小二乘法#
在这个示例中,我们拟合了一个对回归系数施加正约束的线性模型,并将估计的系数与经典线性回归进行比较。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
生成一些随机数据
np.random.seed(42)
n_samples, n_features = 200, 50
X = np.random.randn(n_samples, n_features)
true_coef = 3 * np.random.randn(n_features)
# 将阈值系数调整为非负值
true_coef[true_coef < 0] = 0
y = np.dot(X, true_coef)
# 添加一些噪音
y += 5 * np.random.normal(size=(n_samples,))
将数据分为训练集和测试集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.5)
拟合非负最小二乘法。
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
reg_nnls = LinearRegression(positive=True)
y_pred_nnls = reg_nnls.fit(X_train, y_train).predict(X_test)
r2_score_nnls = r2_score(y_test, y_pred_nnls)
print("NNLS R2 score", r2_score_nnls)
NNLS R2 score 0.8225220806196525
Fit an OLS.
reg_ols = LinearRegression()
y_pred_ols = reg_ols.fit(X_train, y_train).predict(X_test)
r2_score_ols = r2_score(y_test, y_pred_ols)
print("OLS R2 score", r2_score_ols)
OLS R2 score 0.7436926291700346
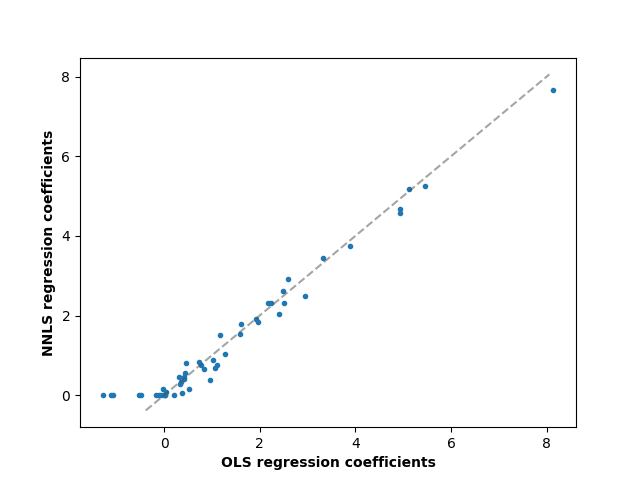
比较OLS和NNLS的回归系数,我们可以观察到它们高度相关(虚线是恒等关系),但非负约束将一些系数缩减为0。非负最小二乘法本质上会产生稀疏结果。
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(reg_ols.coef_, reg_nnls.coef_, linewidth=0, marker=".")
low_x, high_x = ax.get_xlim()
low_y, high_y = ax.get_ylim()
low = max(low_x, low_y)
high = min(high_x, high_y)
ax.plot([low, high], [low, high], ls="--", c=".3", alpha=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel("OLS regression coefficients", fontweight="bold")
ax.set_ylabel("NNLS regression coefficients", fontweight="bold")
Text(55.847222222222214, 0.5, 'NNLS regression coefficients')
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.031 seconds)
Related examples