Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
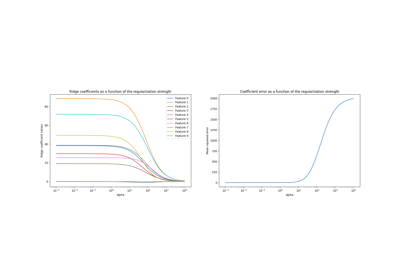
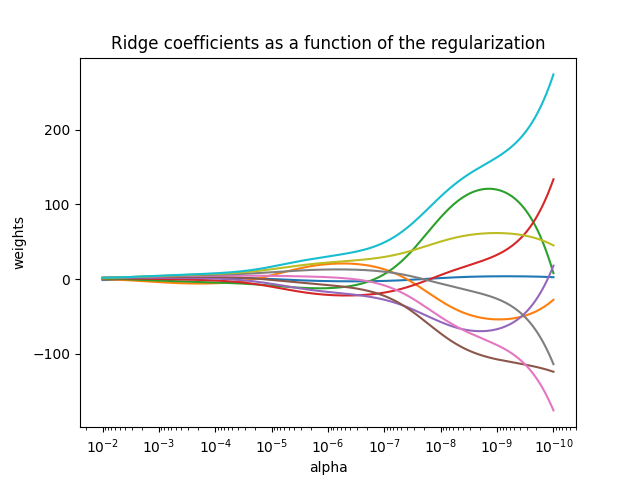
绘制岭回归系数与正则化参数的关系#
展示了共线性对估计器系数的影响。
Ridge 回归是此示例中使用的估计器。
每种颜色代表系数向量的不同特征,并显示为正则化参数的函数。
此示例还展示了将岭回归应用于高度病态矩阵的有用性。 对于此类矩阵,目标变量的轻微变化可能会导致计算权重的巨大方差。 在这种情况下,设置一定的正则化参数(alpha)以减少这种变化(噪声)是有用的。
当 alpha 非常大时,正则化效应主导平方损失函数,系数趋于零。 在路径的末端,随着 alpha 趋向于零,解趋向于普通最小二乘法,系数表现出大的波动。 在实践中,有必要调整 alpha 以在两者之间保持平衡。
# 作者:scikit-learn 开发者
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import linear_model
# X is the 10x10 Hilbert matrix
X = 1.0 / (np.arange(1, 11) + np.arange(0, 10)[:, np.newaxis])
y = np.ones(10)
计算路径#
n_alphas = 200
alphas = np.logspace(-10, -2, n_alphas)
coefs = []
for a in alphas:
ridge = linear_model.Ridge(alpha=a, fit_intercept=False)
ridge.fit(X, y)
coefs.append(ridge.coef_)
显示结果#
ax = plt.gca()
ax.plot(alphas, coefs)
ax.set_xscale("log")
ax.set_xlim(ax.get_xlim()[::-1]) # reverse axis
plt.xlabel("alpha")
plt.ylabel("weights")
plt.title("Ridge coefficients as a function of the regularization")
plt.axis("tight")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.130 seconds)
Related examples