Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
递归特征消除#
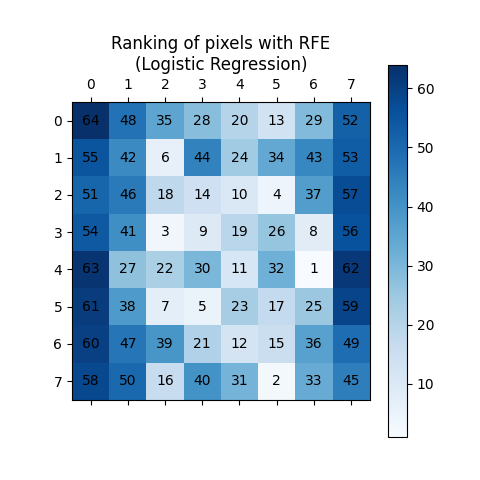
本示例演示了如何使用递归特征消除(RFE )来确定单个像素在手写数字分类中的重要性。RFE 递归地移除最不重要的特征,根据其重要性分配排名,其中较高的 ranking_ 值表示较低的重要性。排名通过蓝色阴影和像素注释进行可视化,以提高清晰度。正如预期的那样,位于图像中心的像素比边缘的像素更具预测性。
Note
另请参见 带交叉验证的递归特征消除
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFE
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
# 加载数字数据集
digits = load_digits()
X = digits.images.reshape((len(digits.images), -1))
y = digits.target
pipe = Pipeline(
[
("scaler", MinMaxScaler()),
("rfe", RFE(estimator=LogisticRegression(), n_features_to_select=1, step=1)),
]
)
pipe.fit(X, y)
ranking = pipe.named_steps["rfe"].ranking_.reshape(digits.images[0].shape)
# 绘制像素排名
plt.matshow(ranking, cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
# 添加像素编号的注释
for i in range(ranking.shape[0]):
for j in range(ranking.shape[1]):
plt.text(j, i, str(ranking[i, j]), ha="center", va="center", color="black")
plt.colorbar()
plt.title("Ranking of pixels with RFE\n(Logistic Regression)")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.426 seconds)
Related examples